Enabling drag reordering in lazy SwiftUI grids and stacks
Aug 30, 2023 ·
While the SwiftUI List supports drag to reordering, LazyVGrid, LazyHGrid, LazyVStack & LazyHStack lack this functionality. Let’s implement this functionality from scratch.
This solution in this post builds upon this amazing post by ramzesenok. I’ve modularized it a bit and added the possibility to provide a custom preview.
What to expect
To give you an idea of what to expect, this will let us enable drag reordering in LazyVGrid and LazyHGrid:

as well as in LazyVStack and LazyHStack, using the same component and configuration:
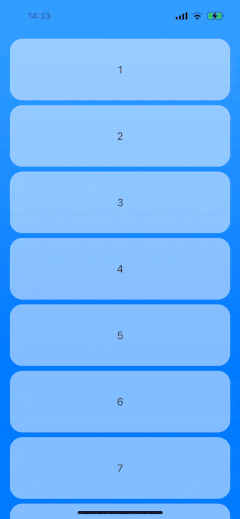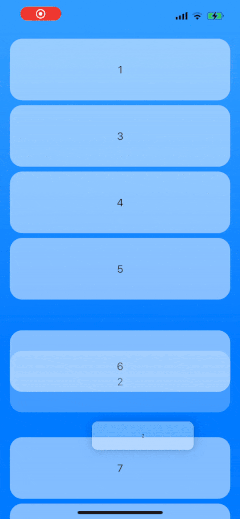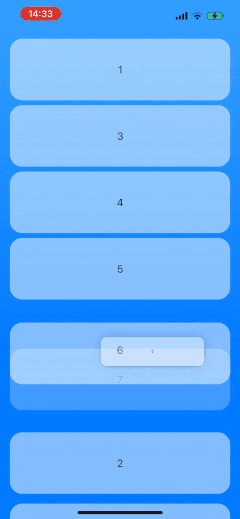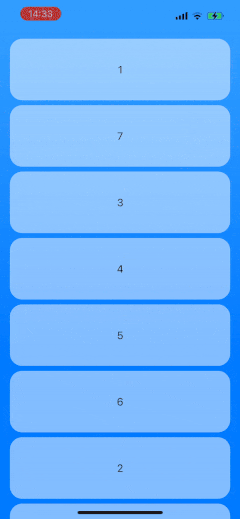
We will be able to use any content views for the list items and customize the preview. The solution will also handle ending the drag gesture outside of the list.
Building the component
Before we start building, we need to specify the capabilities that a reorderable item needs. Let’s call it Reorderable and require it to be both Identifiable and Equatable:
public typealias Reorderable = Identifiable & Equatable
In this post, let’s use a very basic model for our list items, that just has a numeric identifier:
struct GridData: Identifiable, Equatable {
let id: Int
}
Since we want to be able to use this component in all kind of collection views, let’s create it as a replacement to the regular ForEach view. Let’s call it ReorderableForEach:
public struct ReorderableForEach<Item: Reorderable, Content: View, Preview: View>: View {
...
}
We want the view to take a binding to the collection items so we can change the order, a binding to the active item so we can edit it, a content view builder for the list items, a preview builder to customize the drag preview and a moveAction to perform the move:
public struct ReorderableForEach<Item: Reorderable, Content: View, Preview: View>: View {
public init(
_ items: [Item],
active: Binding<Item?>,
@ViewBuilder content: @escaping (Item) -> Content,
@ViewBuilder preview: @escaping (Item) -> Preview,
moveAction: @escaping (IndexSet, Int) -> Void
) {
self.items = items
self._active = active
self.content = content
self.preview = preview
self.moveAction = moveAction
}
public init(
_ items: [Item],
active: Binding<Item?>,
@ViewBuilder content: @escaping (Item) -> Content,
moveAction: @escaping (IndexSet, Int) -> Void
) where Preview == EmptyView {
self.items = items
self._active = active
self.content = content
self.preview = nil
self.moveAction = moveAction
}
@Binding
private var active: Item?
@State
private var hasChangedLocation = false
private let items: [Item]
private let content: (Item) -> Content
private let preview: ((Item) -> Preview)?
private let moveAction: (IndexSet, Int) -> Void
public var body: some View {
... // Coming up
}
}
We can now create a view with and without a custom preview. Let’s now iterate over the collection and render a content view for each item in the collection:
public struct ReorderableForEach<Item: Reorderable, Content: View, Preview: View>: View {
...
public var body: some View {
ForEach(items) { item in
if let preview {
contentView(for: item)
.onDrag {
dragData(for: item)
} preview: {
preview(item)
}
} else {
contentView(for: item)
.onDrag {
dragData(for: item)
}
}
}
}
private func contentView(for item: Item) -> some View {
content(item)
.opacity(active == item && hasChangedLocation ? 0.5 : 1)
.onDrop(
of: [.text],
delegate: ReorderableDragRelocateDelegate(
item: item,
items: items,
active: $active,
hasChangedLocation: $hasChangedLocation
) { from, to in
withAnimation {
moveAction(from, to)
}
}
)
}
private func dragData(for item: Item) -> NSItemProvider {
active = item
return NSItemProvider(object: "\(item.id)" as NSString)
}
}
In this code, we use a plain ForEach to iterate over the items, then render a contentView for each item, with an onDrag modifier applied to let us drag the items.
The drag modifier differs a bit depending on if we want to use a custom preview or not. We thus perform an if check and render the same content view with two different modifiers.
In the contentView builder, we change the opacity when an item is active. We also apply an onDrop modifier with a custom delegate that looks like this:
struct ReorderableDragRelocateDelegate<Item: Reorderable>: DropDelegate {
let item: Item
var items: [Item]
@Binding var active: Item?
@Binding var hasChangedLocation: Bool
var moveAction: (IndexSet, Int) -> Void
func dropEntered(info: DropInfo) {
guard item != active, let current = active else { return }
guard let from = items.firstIndex(of: current) else { return }
guard let to = items.firstIndex(of: item) else { return }
hasChangedLocation = true
if items[to] != current {
moveAction(IndexSet(integer: from), to > from ? to + 1 : to)
}
}
func dropUpdated(info: DropInfo) -> DropProposal? {
DropProposal(operation: .move)
}
func performDrop(info: DropInfo) -> Bool {
hasChangedLocation = false
active = nil
return true
}
}
This delegate will actually try to perform the move as soon as dropEntered is triggered. This is why the items reorder as we drag, as you can see in the gifs above.
This is actually all we need, but we do want some additional handling as well. For instance, we want to be able to terminate the move operation if an item is dropped outside the list.
To do this, let’s create another delegate:
struct ReorderableDropOutsideDelegate<Item: Reorderable>: DropDelegate {
@Binding
var active: Item?
func dropUpdated(info: DropInfo) -> DropProposal? {
DropProposal(operation: .move)
}
func performDrop(info: DropInfo) -> Bool {
active = nil
return true
}
}
All this does is to reset the active state whenever it performs a drop. We can now create a view extension to make it easy to bind this delegate to any view:
public extension View {
func reorderableForEachContainer<Item: Reorderable>(
active: Binding<Item?>
) -> some View {
onDrop(of: [.text], delegate: ReorderableDropOutsideDelegate(active: active))
}
}
This modifier should be applied to the outermost container, to make sure that ending the drag gesture outside the list will still reset the active state.
And with that, we’re done. To use this, just apply the reorderableForEachContainer to the container view, then use a ReorderableForEach instead of a ForEach:
struct ContentView: View {
@State
private var items = (1...100).map { GridData(id: $0) }
@State
private var active: GridData?
var body: some View {
ScrollView(.vertical) {
LazyVGrid(columns: .adaptive(minimum: 100, maximum: 200)) {
ReorderableForEach(items, active: $active) { item in
shape
.fill(.white.opacity(0.5))
.frame(height: 100)
.overlay(Text("\(item.id)"))
.contentShape(.dragPreview, shape)
} preview: { item in
Color.white
.frame(height: 150)
.frame(minWidth: 250)
.overlay(Text("\(item.id)"))
.contentShape(.dragPreview, shape)
} moveAction: { from, to in
items.move(fromOffsets: from, toOffset: to)
}
}.padding()
}
.background(Color.blue.gradient)
.scrollContentBackground(.hidden)
.reorderableForEachContainer(active: $active)
}
var shape: some Shape {
RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 20)
}
}
Remember to apply a .contentShape(.dragPreview, ...) modifier if your list items need a shape when they’re being lifted up, as well as to any custom preview you may want to use.
Happy reordering!
Discussions & More
If you found this interesting, please share your thoughts on Bluesky and Mastodon. Make sure to follow to be notified when new content is published.